 class HCL_LineSearch_d : public HCL_Base
class HCL_LineSearch_d : public HCL_Base  class HCL_LineSearch_d : public HCL_Base
class HCL_LineSearch_d : public HCL_Base Abstract base class for line search routines
| | Parameters () const Access to the parameter table |
| | SetScaling ( const HCL_LinearOp_d * S ) SetScaling allows the specification of a different inner product (and hence norm) |
| | UnSetScaling () UnSetScaling causes the line search to use the default inner product |
| | Search ( HCL_Functional_d & f, const HCL_Vector_d & xcur, HCL_Vector_d & xnext, HCL_Vector_d & dir, HCL_EvaluateFunctional_d * xinit_eval) LineSearch algorithm |
| | Term codes |
Abstract base class for line search routines. The purpose of a line search algorithm is to locate an approximate minimizer of a function. Such problems arise in certain algorithms for unconstrained and constrained optimization, where
is a 1D "slice" of the objective or merit function. The is, the original problem is to minimizer some function
, where
is a Hilbert space, and
is defined by
, where
and
are vectors in
.
The main method in a HCL_LineSearch_d class is Search, which is invoked as follows:
MyFcnl f; // MyFcnl must be derived from HCL_Functional_d MyVector x( "x0" ); // Assume MyVector has a constructor which //reads from a file MyVector y( "direction" ); MyVector * xnext = new MyVector( x ); // Assume MyVector has a copy // constructor. HCL_LineSearch_DS_d lsearch( "lsearch.dat" ); // Dennis-Schnabel // line search HCL_EvaluateFunctional_d * eval = f.EvaluateGrad( x ); HCL_EvaluateFunctional_d * evalnext lsearch.Search( f,x,*xnext,y,eval );Note that it is necessary to evaluate the functional at the initial pointand pass this evaluation object to the Search method. The method attempts to locate a suitable point and return it in the vector pointed to by the pointer xnext. Also, the evaluation object of
is the return value of the method.
Standard line search algorithms are usually based on one or two goals. Essentially all algorithms attempt to reduce the value of the function
from
, usually by satisfying a condition
(the assumption is made that
is negative). The number
in the above inequality is a standard input parameter to a line search algorithm; in HCL this parameter is called FcnDecreaseTol. A second goal which is often sought is the reduction of the slope from
:
The tolerance in this condition is called SlopeDecreaseTol in HCL.
Other important parameters appearing in line search algorithms are MaxSample (the maximum number of times that the function can be sampled before the algorithm gives up), and MinStep and MaxStep (the smallest and largest allowable steps). For a complete list of algorithmic parameters, see the Input parameters documentation for the base class, and for each concrete derived class (note that a specific algorithm may use a parameter not mentioned in the base class).
Algorithmic parameters can be accessed or modified through the Parameters method of the class, which returns a reference to the parameter table (see the Table class for more details about parameter tables):
lsearch.Parameters().GetValue( "MinStep",m ); // Gets the value of // the parameter MinStep // and puts it in m. lsearch.Parameters().PutValue( "MinStep",2*m ); // Sets the value of // the parameter MinStep // to 2*m.In addition, derived line search classes should have constructors which take a file name and read parameters from that file (using the Table file format). All input parameters have default values which are given in the (derived) class documentation.All line searchs are required to set two output parameters in the paramter table, TermCode and MaxTkn. The possible values of TermCode are given by the enum variable ErrorCodes. The documentation of ErrorCodes should be consulted for a complete list of codes, but the following convention is followed: 0 means a succesful completion, a positive values means that the algorithm succeeded in reducing the function value, although the termination criteria were not all satisfied, and a negative value indicates that the search was unable to reduce the function value. MaxTkn is a boolean integer variable; if it is set, this indicates that the step taken was of length MaxStep.
![]() double SlopeDecreaseTol
double SlopeDecreaseTol
![]() double MinStep
double MinStep
![]() double MaxStep
double MaxStep
![]() int MaxSample
int MaxSample
![]() double ZeroDivideTol
double ZeroDivideTol
![]() int DispFlag
int DispFlag
![]() int DumpFlag
int DumpFlag
![]() char DumpFile[81]
char DumpFile[81]
![]() int DispPrecision
int DispPrecision
![]() int DumpPrecision
int DumpPrecision
![]() int MaxTkn
int MaxTkn
![]() virtual Table& Parameters() const
virtual Table& Parameters() const
![]() virtual void SetScaling( const HCL_LinearOp_d * S )
virtual void SetScaling( const HCL_LinearOp_d * S )
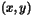 , the scaled inner
product
, the scaled inner
product 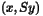 will be used, where
will be used, where 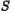 is a symmetric
positive definite operator. Through this method, a line
search can be made consistent with a minimization algorithm which
scales the norm.
is a symmetric
positive definite operator. Through this method, a line
search can be made consistent with a minimization algorithm which
scales the norm.
![]() virtual void UnSetScaling()
virtual void UnSetScaling()
![]() virtual HCL_EvaluateFunctional_d* Search( HCL_Functional_d & f, const HCL_Vector_d & xcur, HCL_Vector_d & xnext, HCL_Vector_d & dir, HCL_EvaluateFunctional_d * xinit_eval)
virtual HCL_EvaluateFunctional_d* Search( HCL_Functional_d & f, const HCL_Vector_d & xcur, HCL_Vector_d & xnext, HCL_Vector_d & dir, HCL_EvaluateFunctional_d * xinit_eval)
xcur - starting point
dir - starting direction
xinit_eval - evaluation object for starting point
alphabetic index hierarchy of classes

this page has been generated automatically by doc++
(c)opyright by Malte Zöckler, Roland Wunderling
contact: doc++@zib.de