 class HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d : public HCL_BiLinearOp_d
class HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d : public HCL_BiLinearOp_d  class HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d : public HCL_BiLinearOp_d
class HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d : public HCL_BiLinearOp_d HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d is a bilinear operator class implementing the second derivative of a nonlinear operator
| | HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d ( const HCL_EvaluateOp_d * ev ) Usual constructor; just needs an operator's evaluation object |
| | Domain1 () const Access to the domain of the first argument |
| | Domain2 () const Access to the domain of the second argument |
| | Range () const Access to the range |
| | Image ( const HCL_Vector_d & x, const HCL_Vector_d & y, HCL_Vector_d & z ) const Image computes the action of the operator on the pair (x,y), giving z. |
| | Write ( ostream & str ) const Write prints a description of the object |
| | PartialAdjImage ( int i, const HCL_Vector_d & xy, const HCL_Vector_d & z, HCL_Vector_d & yx ) const The method PartialAdjImage implements the mappings 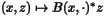 ( (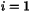 ) and ) and 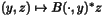 (
(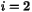 ) )
|
HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d is a bilinear operator class implementing the second derivative of a nonlinear operator. It exists to relieve the implementor of an operator class from the necessity of creating a distinct class to represent the derivative if there is no (efficiency) advantage gained by creating such a class. In order to use this default derivative class, the implementor of the operator class must implement the protected virtual functions SecondDerivImage, SecondDerivPartialAdjImage.The various mechanisms for implementing operator classes, including the use of this default class, are explained in detail, with concrete examples, in the report
"Implementing operators in HCL", Technical Report 99-22, Department of Computational and Applied Mathematics, Rice University, Houston, TX 77251-1892.
downloadable from the HCL home page.
This class is concrete: all of its methods are implemented, and are not intended to be overridden.
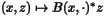 (
(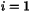 ) and
) and  (
( ). It is implemented to enable the use of the default linear
operator class HCL_RestrictedBiLinearOp_d to represent the
operators Op1, Op2, Op3.
). It is implemented to enable the use of the default linear
operator class HCL_RestrictedBiLinearOp_d to represent the
operators Op1, Op2, Op3.
![]() HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d( const HCL_EvaluateOp_d * ev )
HCL_OpDefaultSecondDeriv_d( const HCL_EvaluateOp_d * ev )
![]() virtual HCL_VectorSpace_d& Domain1() const
virtual HCL_VectorSpace_d& Domain1() const
![]() virtual HCL_VectorSpace_d& Domain2() const
virtual HCL_VectorSpace_d& Domain2() const
![]() virtual HCL_VectorSpace_d& Range() const
virtual HCL_VectorSpace_d& Range() const
![]() virtual void Image( const HCL_Vector_d & x, const HCL_Vector_d & y, HCL_Vector_d & z ) const
virtual void Image( const HCL_Vector_d & x, const HCL_Vector_d & y, HCL_Vector_d & z ) const
![]() virtual ostream& Write( ostream & str ) const
virtual ostream& Write( ostream & str ) const
alphabetic index hierarchy of classes

this page has been generated automatically by doc++
(c)opyright by Malte Zöckler, Roland Wunderling
contact: doc++@zib.de